Receive the latest news and updates about Thyroid Eye Disease (TED).

An easy-to-use guide to help you spot TED and make a differential diagnosis.
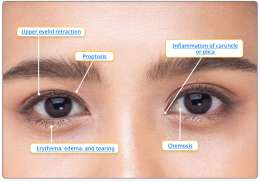
An interactive tool used to make a differential diagnosis of TED.
Use the Patient Intake Form to help measure the impact TED has on your patient’s activities of daily living and emotional well-being.

Have questions about TED? Sign up to speak with an Amgen representative.

Interested in learning more about TED? Get the latest updated information delivered straight to your inbox.
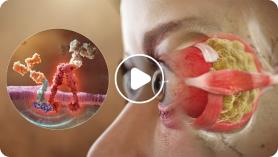
Go behind the eye to uncover the pathophysiology of TED.
Chapter 1: Pathophysiology of Thyroid Eye Disease (TED)
Thyroid Eye Disease, or TED, is a serious, progressive, and vision-threatening autoimmune disease. Emerging research demonstrates that the orbital fibroblast, a specialized cell responsible for tissue repair, is central to the pathophysiology of TED.1-4
Pathogenic orbital fibroblasts are believed to recruit fibrocytes and lymphocytes that infiltrate the orbit.4,5
Fibrocytes differentiate into orbital fibroblasts, which enhance T-cell proliferation and activation.2,4,6
T-cells and B-cells activate orbital fibroblasts and secrete cytokines, thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor, or TSHR, autoantibodies, and insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor, or IGF-1R, autoantibodies, which contribute to the inflammatory cascade.4,7
Two co-localized receptors reside on the surface of orbital fibroblasts: TSHR and IGF-1R, a gatekeeper of orbital fibroblast activation.2,4,8-10
Autoantibodies activate TSHR and IGF-1R, and cross talk mediated by beta-arrestin creates a receptor-signaling complex that stimulates orbital fibroblasts.4,11
Chapter 2: Inflammatory Cascade and Potential Consequences of TED
Once activated, orbital fibroblasts proliferate and produce inflammatory cytokines and hydrophilic hyaluronan, which enlarges orbital tissue volume.1,4
Activated orbital fibroblasts differentiate into adipocytes and myofibroblasts, which contribute, respectively, to adipogenesis and fibrosis of the orbital tissues.4,12
The ensuing tissue expansion and remodeling leads to crowding in the fixed bony orbit, and this may have long-term sequelae.4
Damage can include:
Cross talk between TSHR and IGF-1R, as well as IGF-1R-mediated immune function, may play a critical role in the pathophysiology of TED.
Understanding the cross talk may be vital to addressing this debilitating disease.4,10,16
REFERENCES: